Abstract
Background. The population ageing can be considered both a medical success and a challenge to our society. According to the World Health Organization, people aged 60 or more will reach to 2,000 million in 2050, this is, 22% of the world population. Therefore, it is expected an increased amount of institutionalized elderly in the coming years.
Objectives: our study was aimed to assess and describe the functionality, health, and quality of life of institutionalized older adults as well as to analyze the influence of their dependence level on these variables.
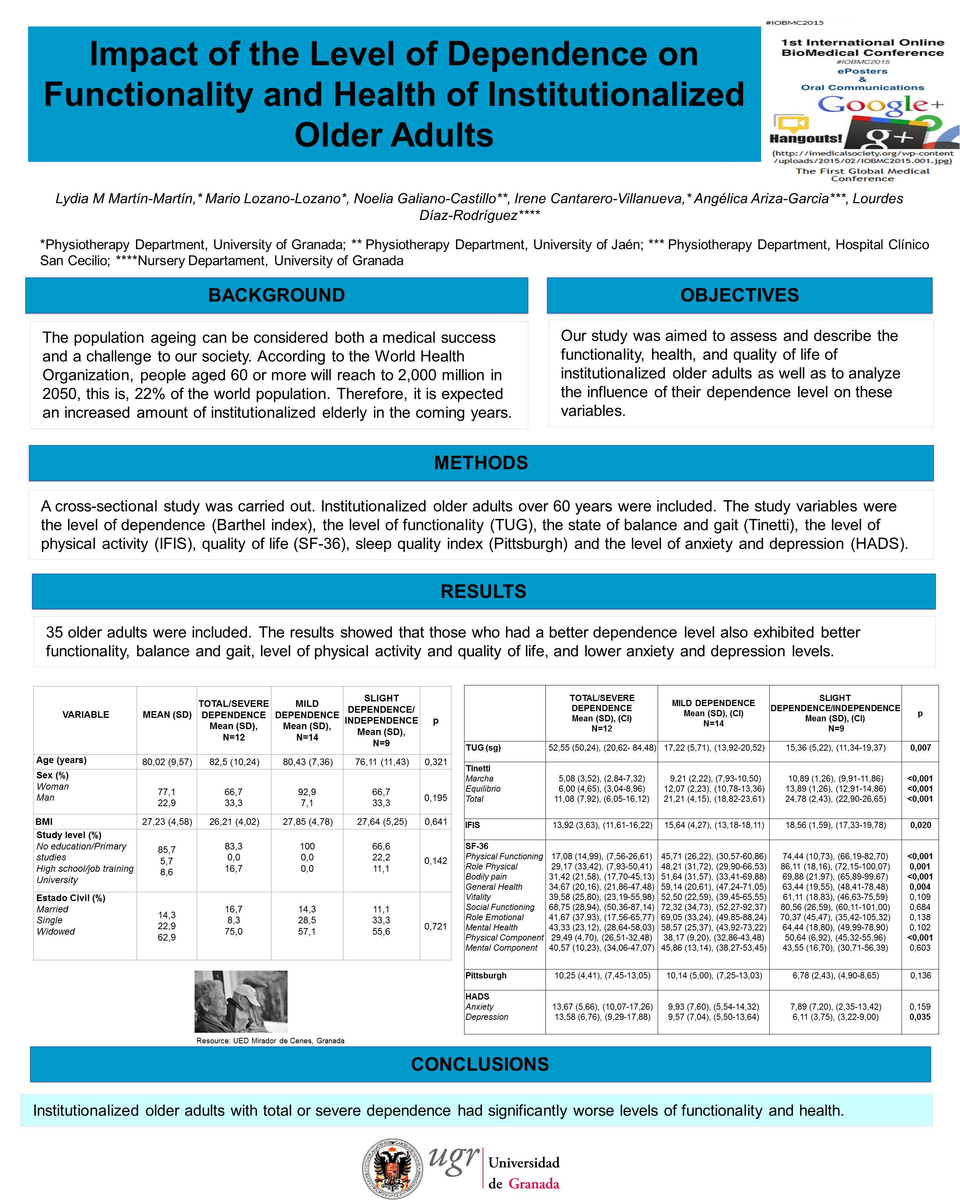
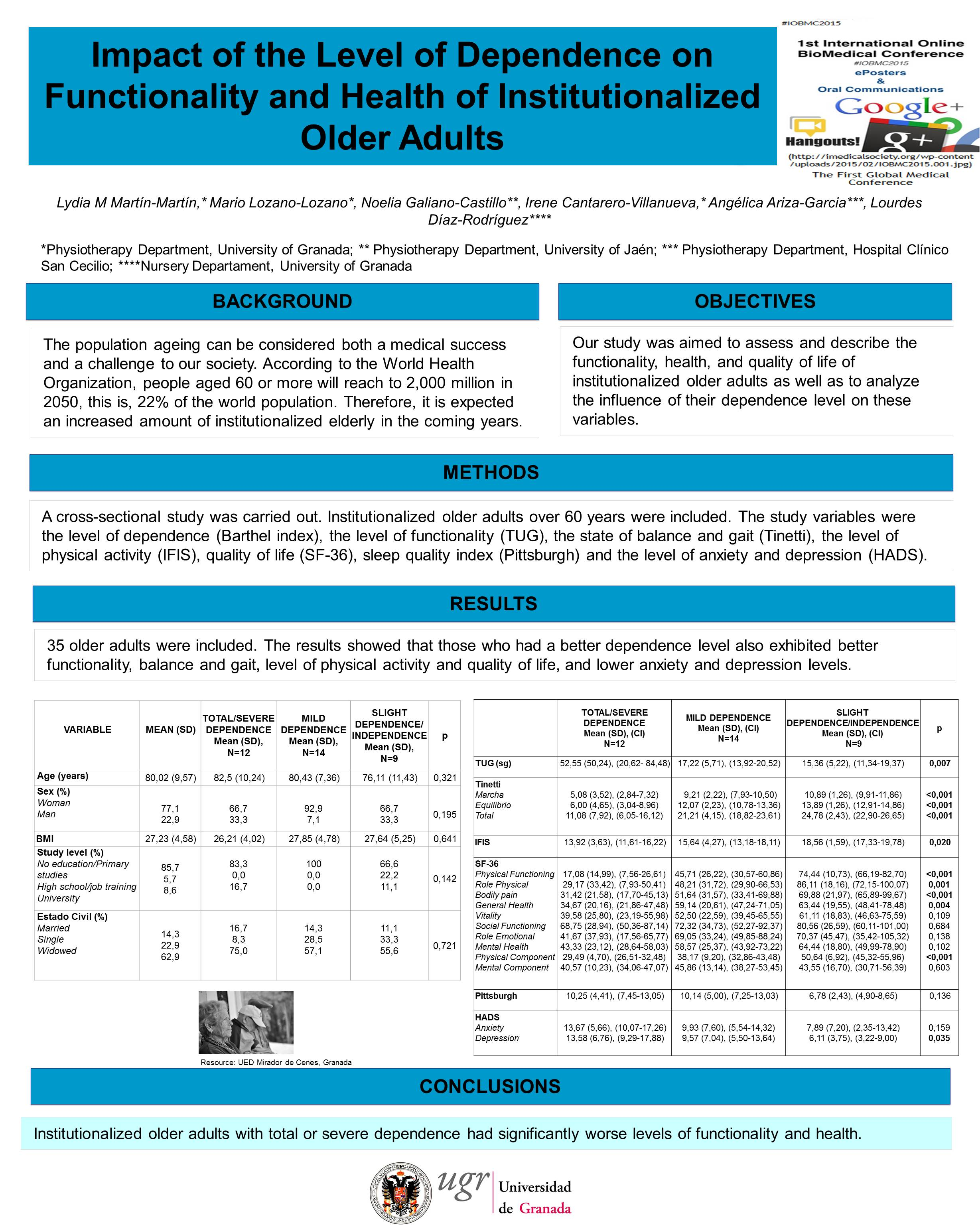
Methods. A cross-sectional study was carried out. Institutionalized older adults over 60 years were included. The study variables were the level of dependence (Barthel index), the level of functionality (TUG), the state of balance and gait (Tinetti), the level of physical activity (IFIS), quality of life (SF questionnaire 36), sleep quality index (Pittsburgh) and the level of anxiety and depression (HADS).
Results. 35 older adults were included. The results showed that those who had a better dependence level also exhibited better functionality, balance and gait, level of physical activity and quality of life, and lower anxiety and depression levels.
Conclusions. Institutionalized older adults with total or severe dependence had significantly worse levels of functionality and health.