Abstract
Background
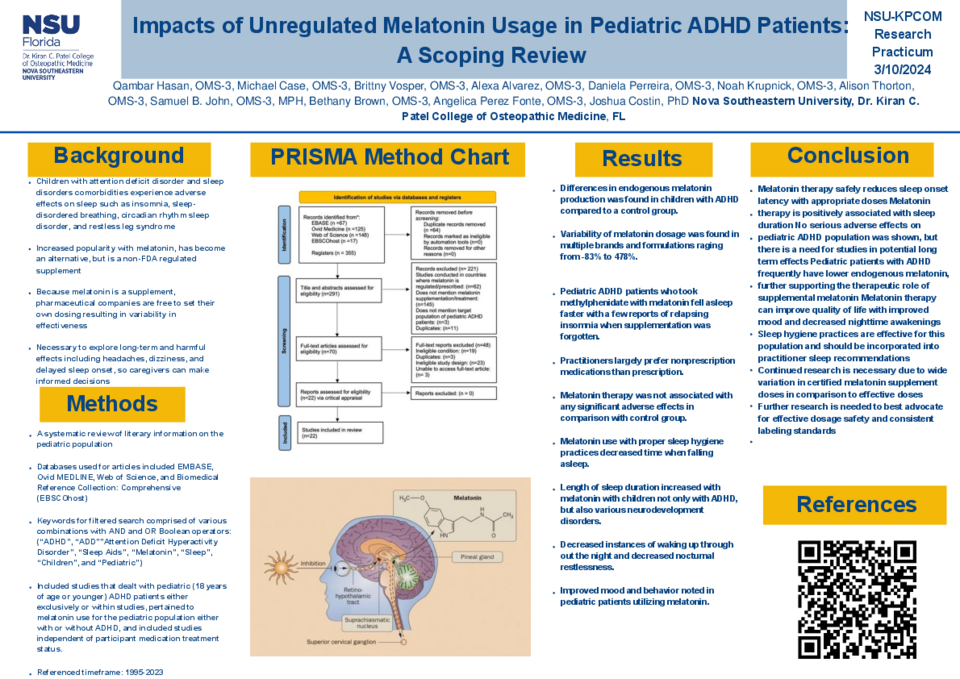
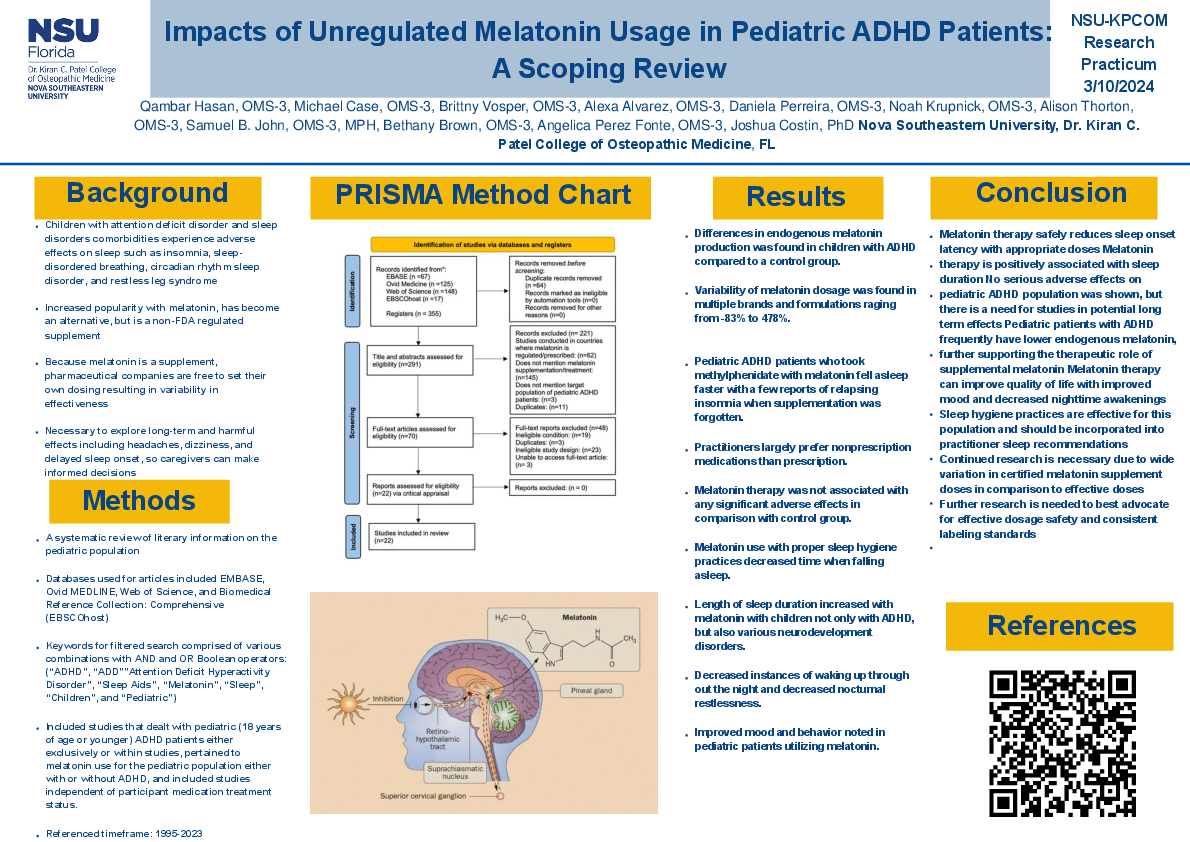
An estimated 5% of children have a diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Many of these children also experience sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep-disordered breathing, and more. Melatonin is a popular over-the-counter sleep aid. However, since it is considered a supplement, it is not regulated by the FDA. Thus, companies set their parameters for dosing. Independent FDA research found that supplements often contained substances not indicated on the label. There is a lack of evidence for long and short-term use of melatonin in conjunction with pharmacotherapy for ADHD.
Objective
The goal of this scoping review is to investigate if OTC melatonin supplementation is safe and effective for children and adolescents with ADHD.
Methods
In October 2023, a search for articles was conducted using EMBASE, Ovid MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Biomedical Reference Collection: Comprehensive. Searches combined the following terms in various combinations with AND and OR Boolean operators: “ADHD”, “ADD”, “Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder”, “Sleep Aids”, “Melatonin”, “Sleep”, “Children”, and “Pediatric”. Only studies in English or translated into English were used. The studied population included pediatric patients under 18 with ADHD and concurrent sleep disorders.
Results:
Sleep disorders may affect up to 84% of pediatric ADHD patients. Regarding melatonin therapy, robust evidence supports that melatonin administration can decrease the time to fall asleep (sleep onset latency). Moreover, melatonin may be superior to placebo combined with proper sleep hygiene practices when assessing sleep onset latency. Melatonin may facilitate an increase in sleep duration among patients with neurodevelopmental disorders. Melatonin therapy was not associated with any significant adverse effects. However, certified melatonin content within supplements ranged from an entire lack of melatonin to more than quadruple the labeled dose.
Conclusions:
When administered within an appropriate dose, melatonin therapy is a safe method to reduce sleep onset latency, and may also provide benefits in total sleep duration. However, there remains wide variation in certified melatonin doses within supplements and actual effective doses, and further research should examine how to advocate for better dose safety and labeling standards.