Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive form of brain tumor in adults and its epidemiology is poorly understood. This study will analyze geographic variation and temporal trends of GBM incidence in the United States (US).
Materials and Methods: Age-adjusted GBM rates were extracted from the SEER research plus program for years 2000-2017 (N=75047). Rates were aggregated into states and subregions, which were categorized according to US Census Bureau definitions. Statistical analysis was conducted in Python (Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE).
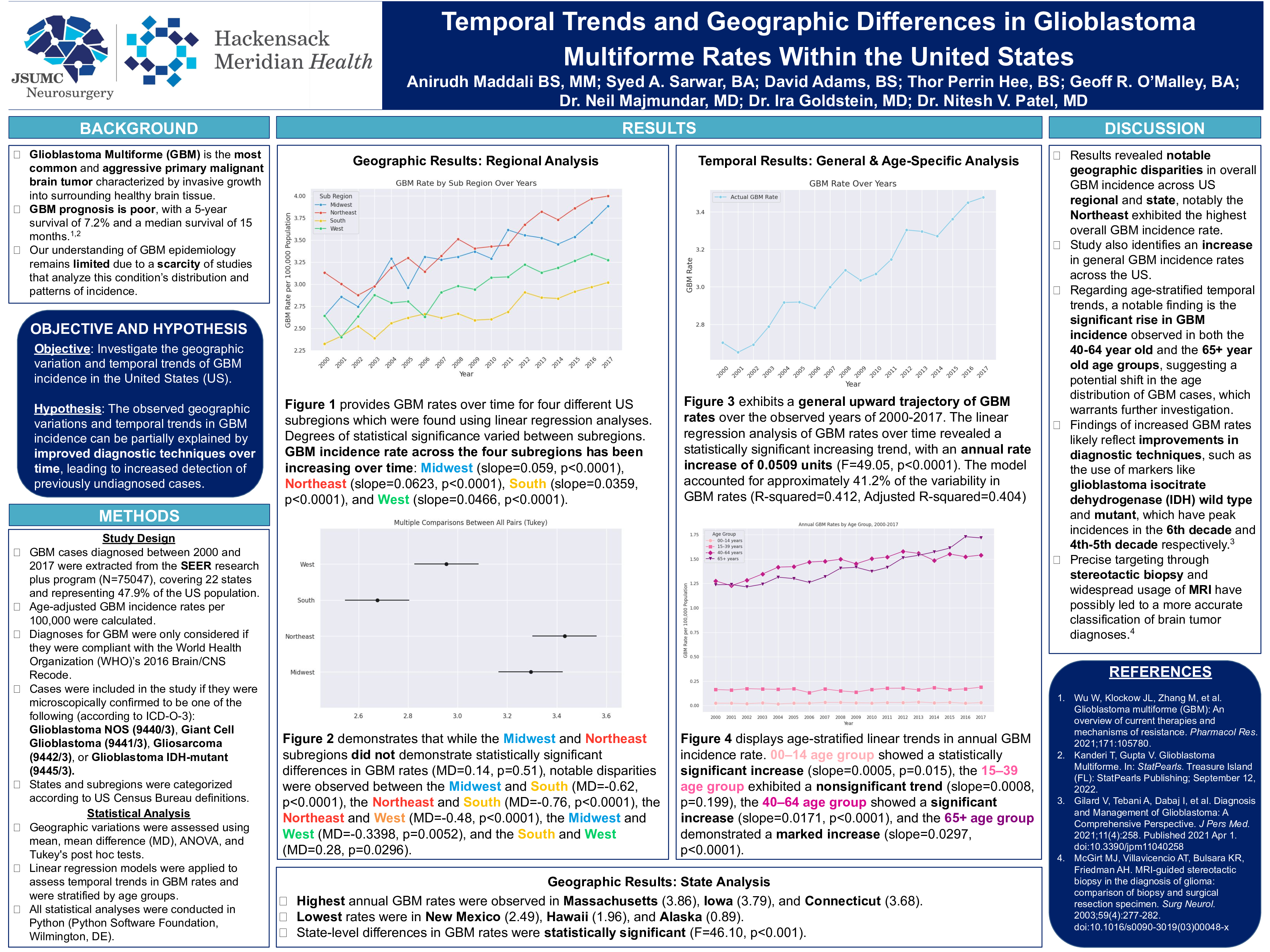
Results: The annual GBM rate for each subregion is: Northeast=3.43, Midwest=3.29, West=2.95, and South=2.68. The differences between regions were statistically significant (F=24.04, P<0.00001). Statistically significant disparities were observed in all pairwise combinations between the four regions except between the Midwest and Northeast. The highest annual GBM rates were observed in Massachusetts (3.86), Iowa (3.79), and Connecticut (3.68), while the lowest rates were in New Mexico (2.49), Hawaii (1.96), and Alaska (0.89). These state-level differences in GBM rates were statistically significant (F=46.10, p<0.001). The annual GBM incidence rate across the US has been increasing over time (F=49.05, p<0.0001, slope=0.051). Similar trends were observed across subregions: Midwest (slope=0.059, p<0.0001), Northeast (slope=0.0623, p<0.0001), South (slope=0.0359, p<0.0001), and West (slope=0.0466, p<0.0001).
Conclusions: Observed increases in annual GBM incidence rates across the US and the geographic differences may be due to improvements in diagnostic capabilities, however these findings do not preclude additional factors such as environmental factors being involved in these differences.