Abstract
Purpose: Most recurrences after primary prostate cancer radiation therapy originate from dominant intraprostatic lesions (DILs). Prostate multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (mpMRI) to target DILs during radiation planning has been shown to improve clinical outcomes for patients in the FLAME trial. 18-Fluorine Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen-1007 (18F PSMA-1007) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) can also target DILs and offers the further opportunities for targeted dose escalation.
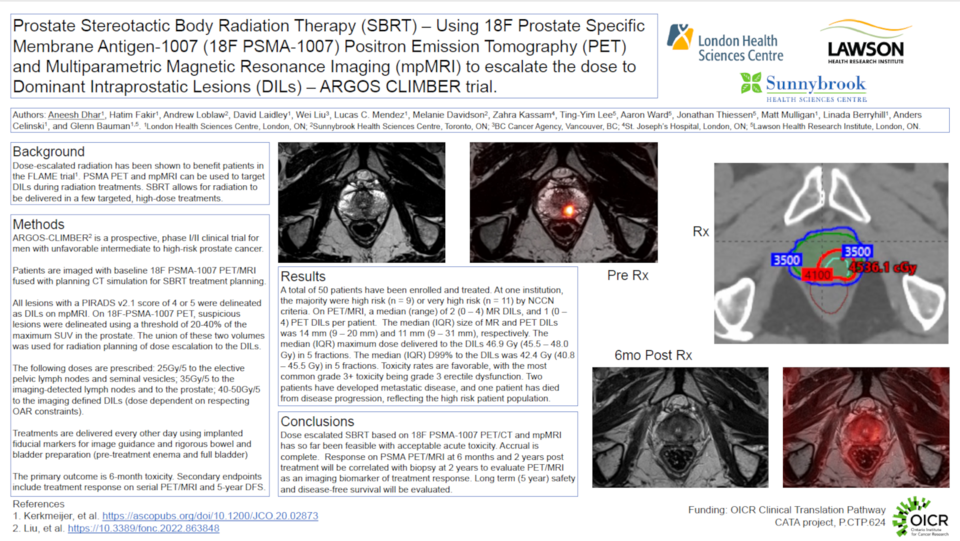
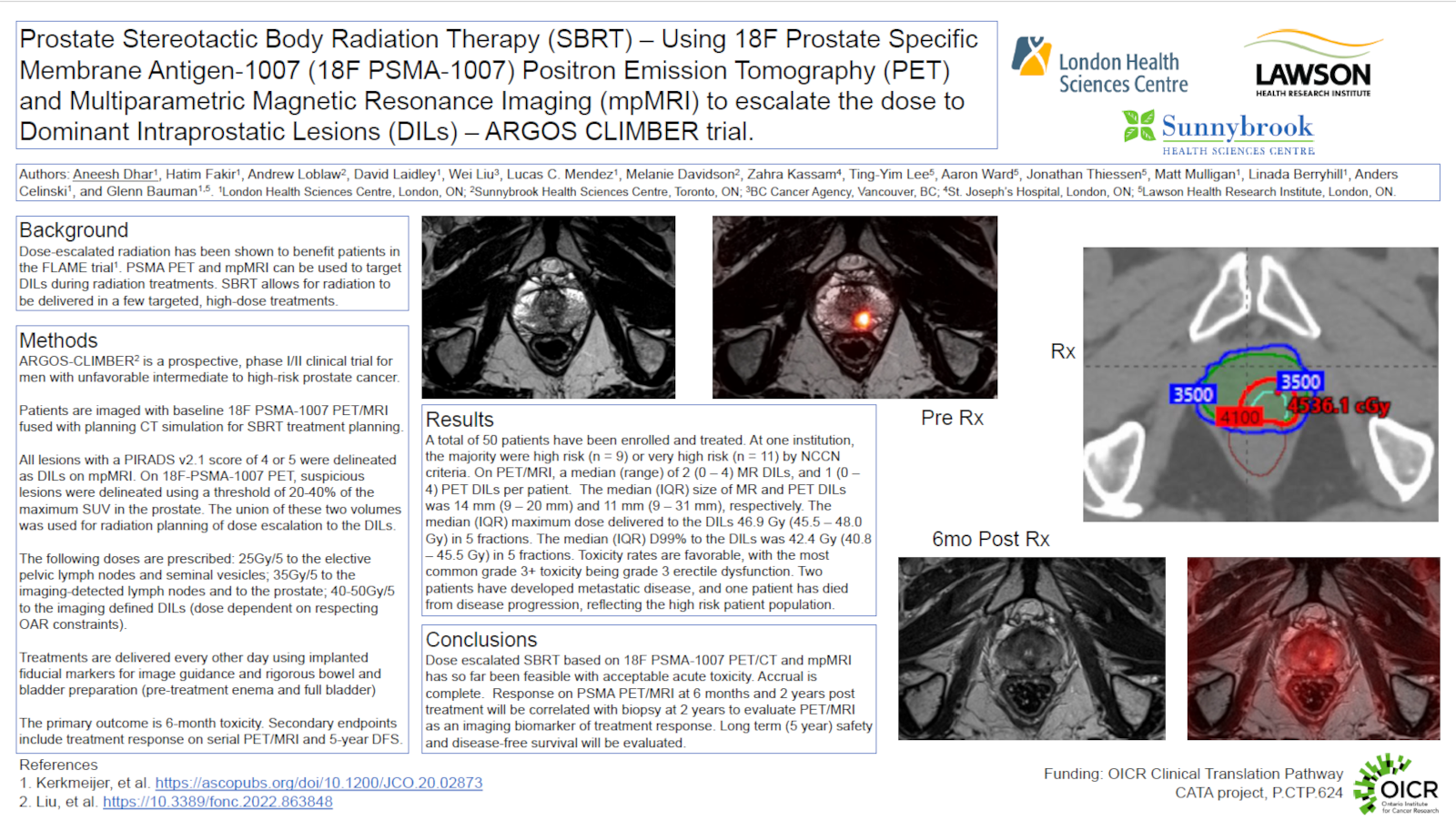
Materials and Methods: ARGOS-CLIMBER is a prospective phase I/II trial enrolling 50 patients with unfavourable intermediate or high-risk disease across two Ontario centres. A hybrid PET/MR scanner was used to acquire co-registered 18F PSMA-1007 PET and mpMRI images prior to stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). The images were rigidly fused with the computed tomography (CT) simulation scans. All patients received intra-prostatic fiducial markers. All DILs were delineated on mpMRI and PET images: on mpMRI, DILs were delineated in areas with low T2 signal and restricted diffusion, and included all lesions with a score of 4 or 5 on the Prostate Image Reporting And Data System (PIRADS v2.1); on 18F PSMA-1007 PET, DILs were delineated automatically by using a Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) threshold of 20-40% of the maximum SUV in the prostate, then this volume was manually edited to the anatomy of the DIL on mpMRI or CT. Final DIL volumes were the union of PET and mpMRI volumes. Planning targets were as follows: whole prostate 35Gy/5; seminal vesicles and elective nodal regions 25Gy/5; imaging involved nodes 35Gy/5; DILs up to 50Gy/5, while respecting organ at risk constraints. Patients were treated every other day with cone beam CT guidance and 6-18 months of adjuvant androgen deprivation. The primary outcome is chronic (6 month) toxicity. Secondary outcomes include acute (6 week) toxicity, quality of life metrics and cancer control outcomes including biopsy clearance at 2 years. PET, mpMRI and biologic biomarkers at 6 months and 2 years post treatment are exploratory endpoints.
Results: Between May 2022 and January 2023, 20 patients have been enrolled, with 18 patients having completed treatment. There were 29 and 34 DILs detected on mpMRI and 18F PSMA-1007 PET, respectively, with a median (range) of 2 (0 – 4) MR DILs and 1 (0 – 4) PET DILs per patient. The median (IQR) size of the MR and PET DILs was 14 mm (9 – 20 mm) and 11 mm (9 – 31 mm). The median (IQR) maximum dose delivered to the combined DIL was 46.9 Gy (45.5 – 48.0 Gy), and the median (IQR) D99% to this volume was 42.4 Gy (40.8 – 45.5 Gy). No patients experienced grade 3+ acute toxicity thus far.
Conclusions: Dose escalation to multi-modality imaging defined DILs on ARGOS/CLIMBER has been feasible with acceptable acute toxicity. Accrual completion is expected by Q2 2023, with the 6-month primary endpoint of GI/GU toxicity available by Q4 2023.