Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most common cancer affecting women, thus it is essential to detect it early to reduce mortality. The objective of this systematic review is to determine the efficacy of utilizing AI networks to examine thermographic breast images to improve the accuracy of detection and earlier detection of breast cancer.
Methods: This systematic review included a database search of PubMed including the terms: imaging, breast cancer screening, diagnosis, detection, artificial intelligence, and women. 5 of the publications met the inclusion criteria and were included in this review.
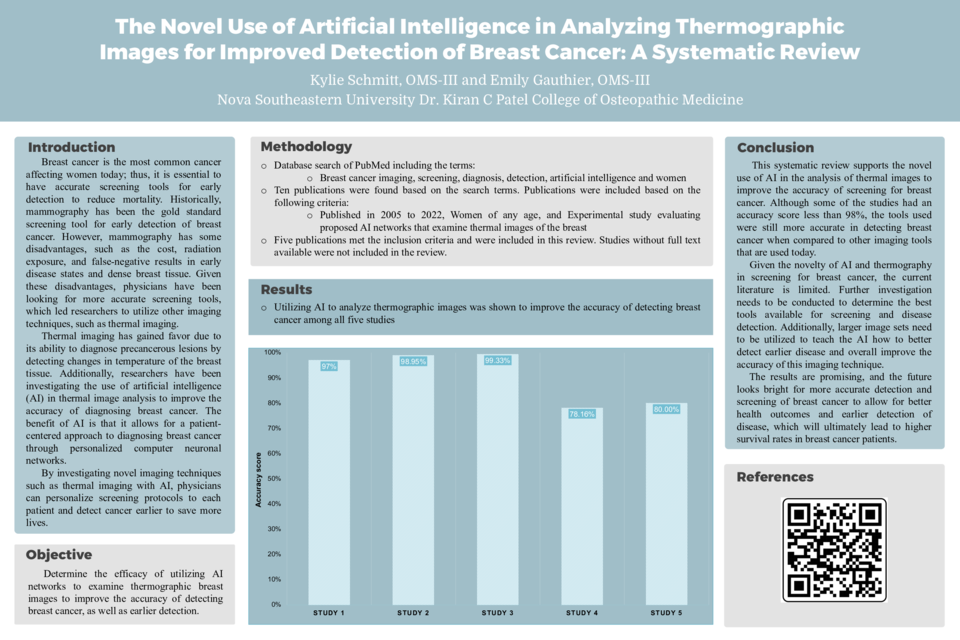
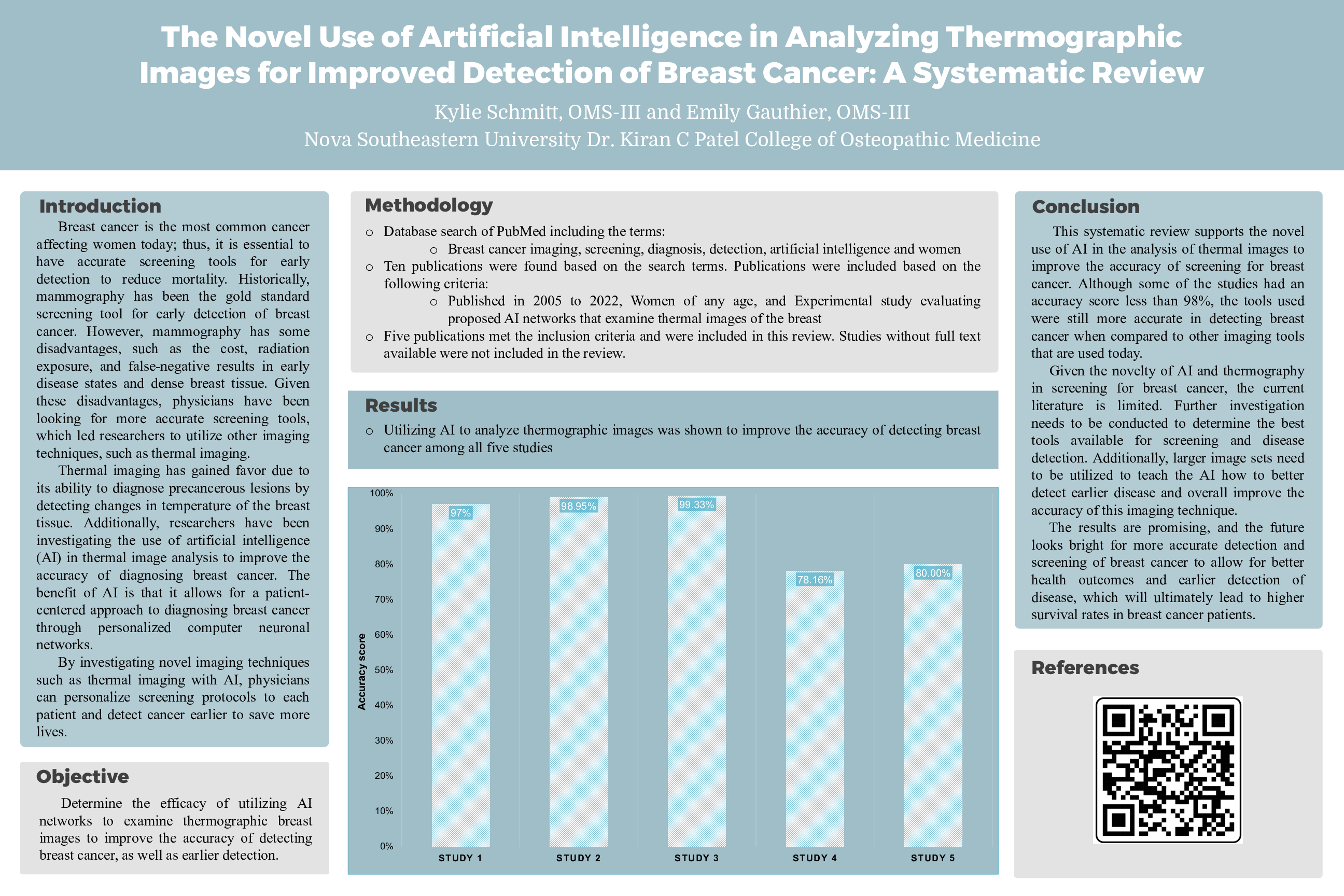
Results: Following an analysis of the existing literature, the use of AI was shown to improve the accuracy of detecting breast cancer. All other studies had an accuracy score ranging from greater than 70%.
Conclusion: This systematic review supports the use of AI in the analysis of thermal images for more accurate detection of breast cancer. These results warrant further investigation and examination of larger image sets and other AI techniques to determine the best tools available for screening and disease detection. These promising findings of more accurate detection of disease through novel imaging techniques with computer-assisted analysis allow for better health outcomes and earlier detection of disease, which can ultimately lead to higher survival rates in breast cancer patients.