Abstract
Purpose: A rapid review was used to determine whether listening to Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR) sounds will help alleviate symptoms of tinnitus.
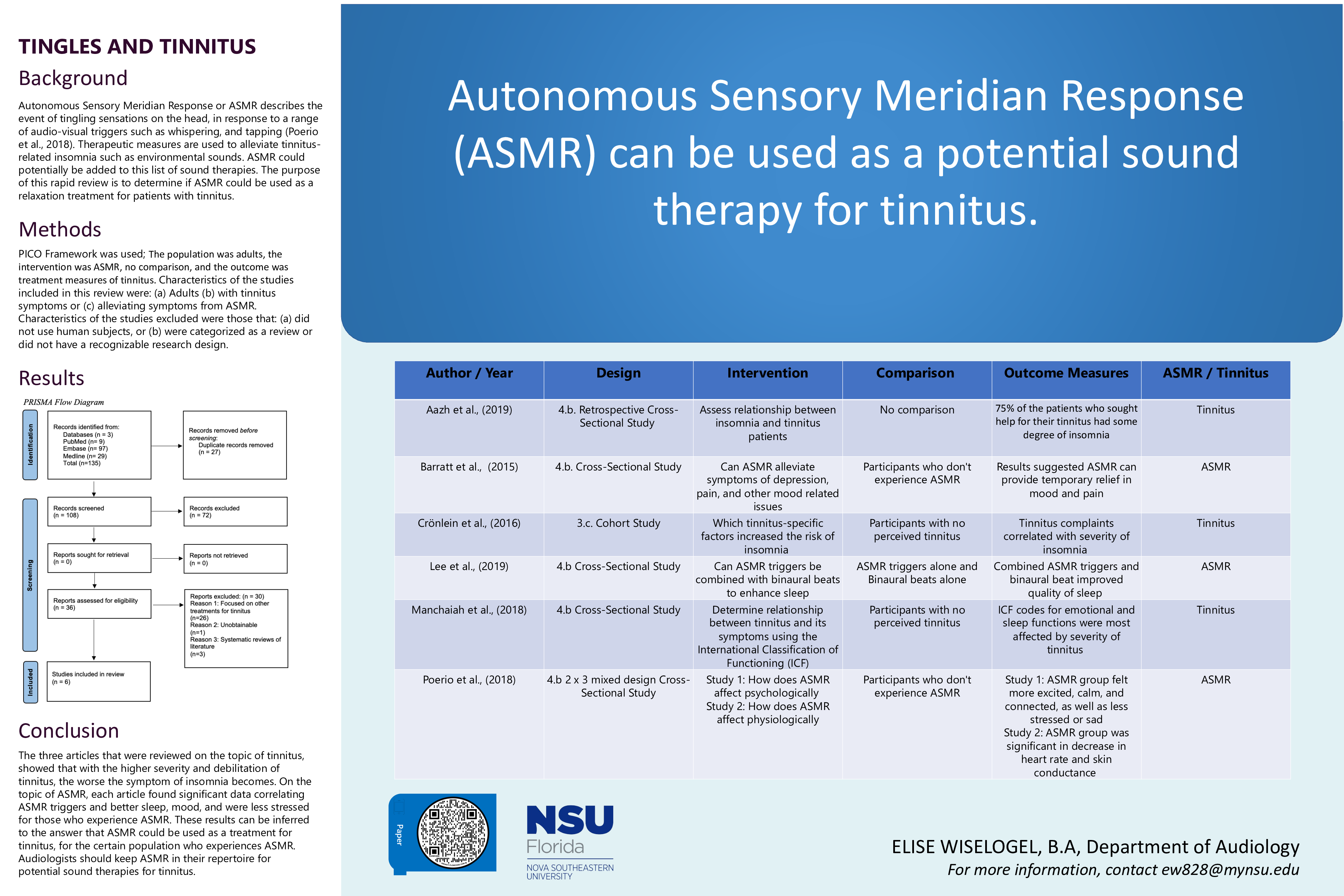
Methods: Using a PICO framework, search terms were generated into three databases; ‘MEDLINE’, ‘Embase’, and ‘Cochrane Central.’ The population was adults, the intervention was ASMR, no comparison, and the outcome was treatment measures of tinnitus. Inclusion criteria for the articles were: published in the last 10 years, noted ASMR with outcomes of relaxation and sleep, or noted tinnitus with the symptoms being stress or insomnia. A PRISMA chart was created to track the selection process.
Results: Data extraction from all three databases yielded 135 articles (29: MEDLINE, 97: Embase, 9: Cochrane Central) as shown in PRISMA Figure 1. Final evaluation indicated 6 articles that met all standards for this rapid literature review. Three articles about ASMR and its benefits on sleep or relaxation were chosen, and three articles about debilitating symptoms of tinnitus, specifically insomnia were selected.
Conclusion: The results can be inferred to the answer that ASMR could be used as a treatment for tinnitus, for the certain population who experiences ASMR.