Abstract
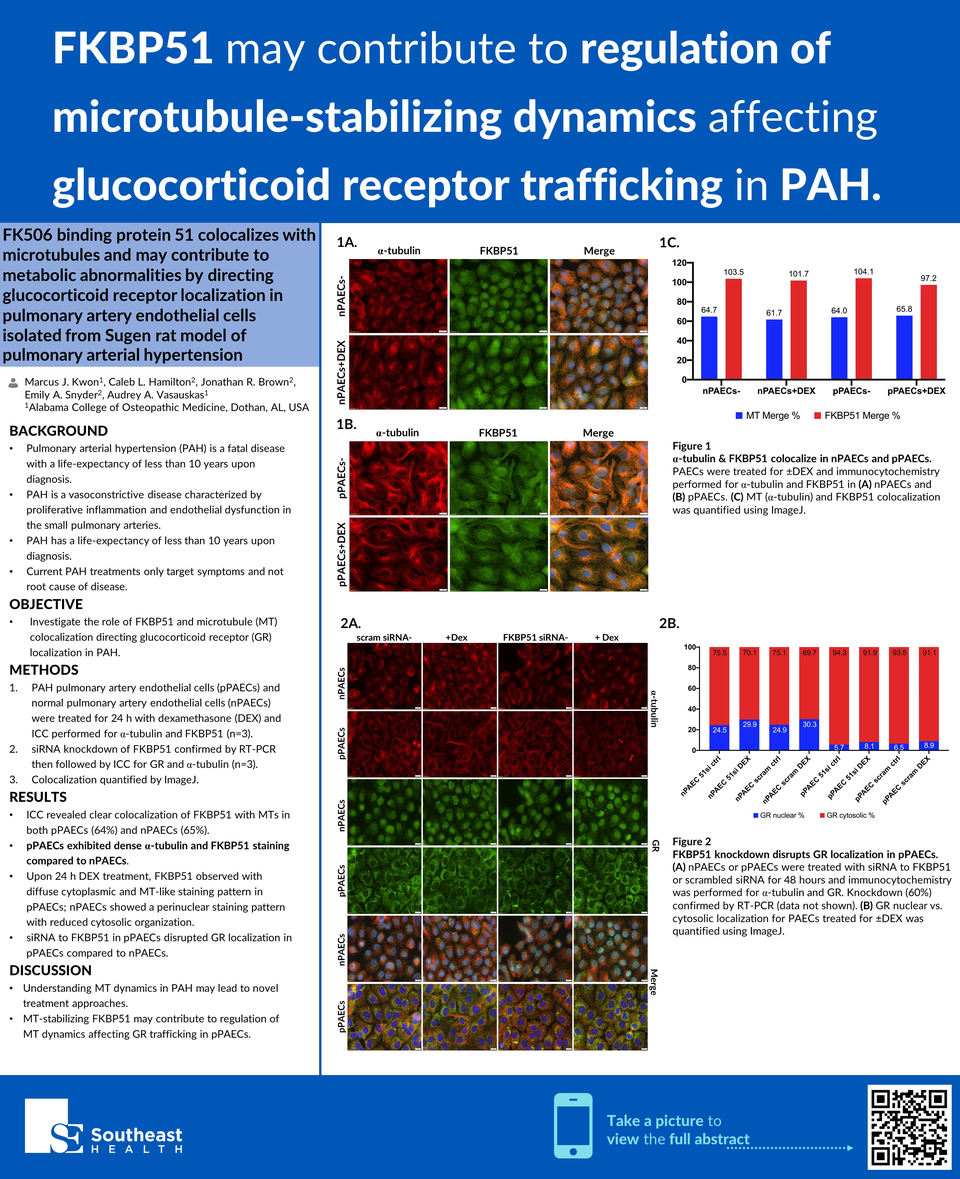
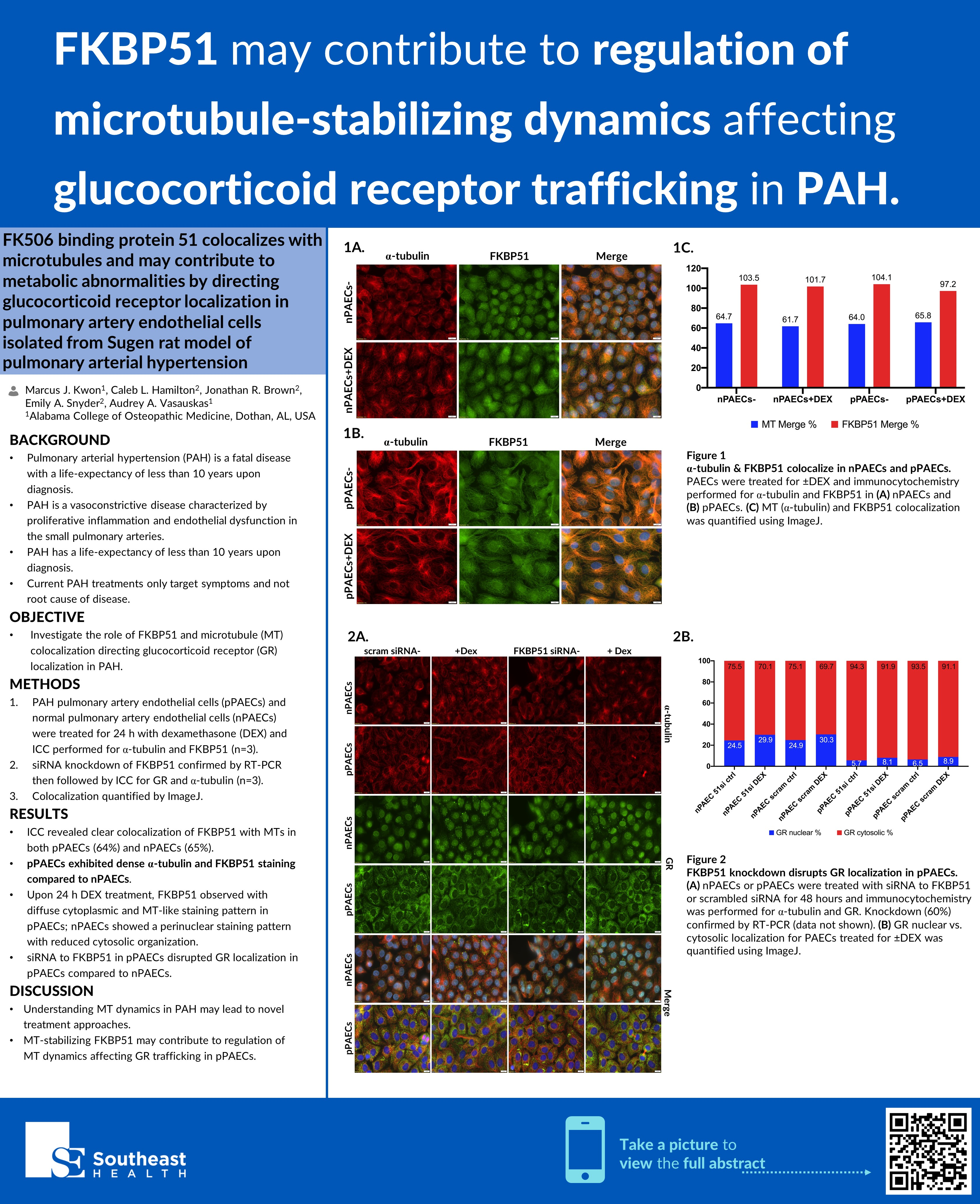
Background: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a fatal vasoconstrictive disease characterized by proliferative inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and metabolic abnormalities in the small pulmonary arteries. While treatments are improving, prognosis remains grim. Immunophilin FKBP51 regulates glucocorticoid receptor (GR), binds to Hsp90, and stabilizes microtubules (MT) in normal pulmonary artery endothelial cells (nPAECs). Prior work indicates increased metabolism of PAH pulmonary artery endothelial cells (pPAECs) and MT abnormalities.
Methods: pPAECs and nPAECs were gifted from the University of South Alabama. Cells were treated for 24 h with dexamethasone (DEX) and ICC performed for α-tubulin and FKBP51 (novel mAb). siRNA was used to knockdown FKBP51 (confirmed by RT-PCR), and ICC for GR and α-tubulin was performed. Colocalization was quantified by ImageJ.
Results: ICC revealed colocalization of FKBP51 with MTs in both pPAECs (64%) and nPAECs (65%). This is the first report showing clear MT staining pattern of FKBP51. pPAECs exhibited dense α-tubulin and FKBP51 staining compared to nPAECs. Upon 24 h DEX, FKBP51 is observed with diffuse cytoplasmic and MT-like staining pattern in pPAECs, whereas nPAECs showed a perinuclear staining pattern with reduced cytosolic organization. siRNA to FKBP51 in pPAECs disrupted GR localization in pPAECs compared to nPAECs.
Conclusions: pPAECs exhibit aberrant metabolism compared to nPAECs and are mechanistically poorly understood. Our data suggests MT-stabilizing FKBP51 may contribute to metabolic changes through regulation of MT dynamics affecting GR trafficking, potentially leading to novel treatment approaches as targeting MT has proven efficacious in treating other proliferative inflammatory diseases.
Supported by R15HL137135-01A1.