Abstract
Background
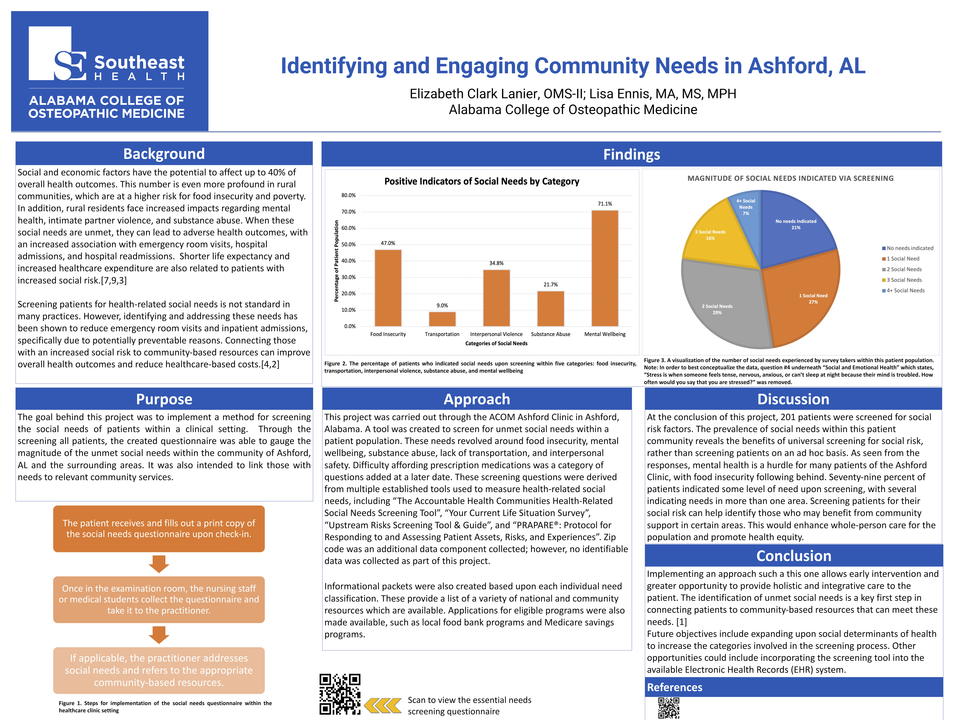
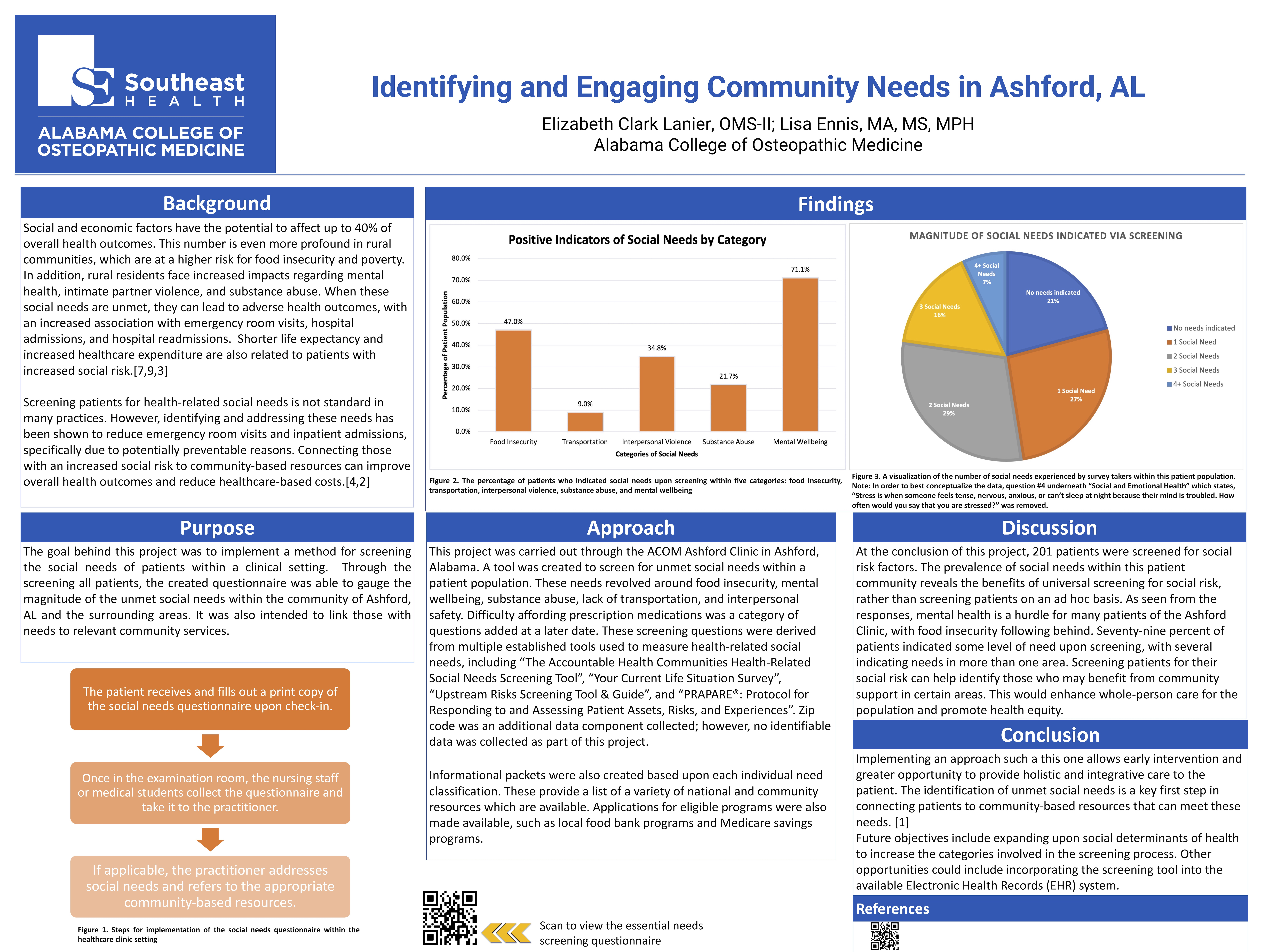
Social and economic factors can affect up to 40% of overall health outcomes. Rural communities face even higher rates of unmet health-related social needs, which, when left unmet, can lead to increased adverse health effects. Screening patients for these social needs is not standard in many practices, but it has proven benefit to those with social risk.
Purpose
The purpose of this project was to engage with vulnerable members of the Wiregrass community through implementing a method for screening and engaging the social needs of patients in a clinic setting.
Approach
This objective was approached initially by creating a survey which assessed for specific essential needs within the community, such as mental health, domestic violence, substance use dependence, food insecurity, ability to afford medications, and lack of transportation access. The Essential Needs Screening Tool is an anonymous screening tool created from multiple previously established tools which measure health-related social needs. A variety of informational resources were created and assembled, which encompassed local and national resources available for each individualized need. A plan was then implemented at the Ashford Clinic in Ashford, Alabama utilizing the surveys and resources to provide information to those patients who screened positively for these essential needs.
Findings
At the conclusion of data collection, 201 total patients were screened for health-related essential needs. Mental wellbeing was experienced by the majority of patients, with food insecurity experienced by almost half of patients. Additionally, 27% of patients screened positively for 1 social need, 29% for 2 social needs, and 16% for 3 social needs.
Conclusion
Identifying unmet social needs is the first step to connecting patients to community-based resources, allowing for early intervention and an increased opportunity to provide holistic and integrative care.