Abstract
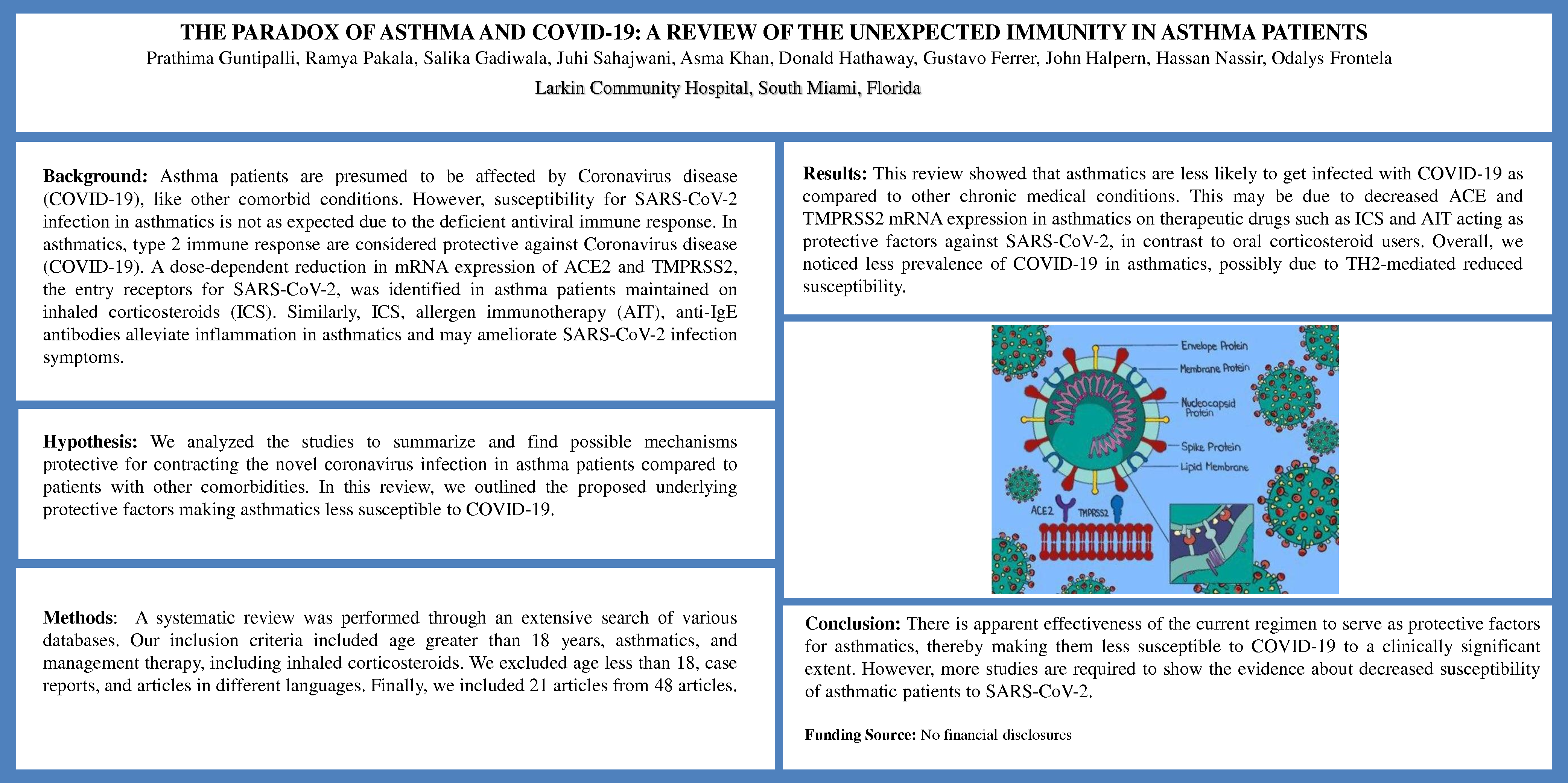
Background: Asthma patients are presumed to be affected by Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), like other comorbid conditions. However, susceptibility for SARS-CoV-2 infection in asthmatics is not as expected due to the deficient antiviral immune response. In asthmatics, type 2 immune responses are considered protective against COVID-19. A dose-dependent reduction in mRNA expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2, the entry receptors for SARS-CoV-2 was identified in asthma patients maintained on inhaled corticosteroids (ICS). Similarly, ICS, allergen immunotherapy (AIT), anti-IgE antibodies alleviate inflammation in asthmatics and may ameliorate SARS-CoV-2 infection symptoms.
Hypothesis: We analyzed the studies to summarize and find possible mechanisms protective for contracting the novel coronavirus infection in asthma patients compared to patients with other comorbidities. In this review, we outlined the proposed underlying protective factors making asthmatics less susceptible to COVID-19.
Methods: A systematic review was performed through an extensive search of various databases. Our inclusion criteria included age greater than 18 years, asthmatics, and management therapy, including inhaled corticosteroids. We excluded age less than 18, case reports, and articles in different languages. Finally, we included 21 articles from 48 articles.
Results: This review showed that asthmatics are less likely to get infected with COVID-19 as compared to other chronic medical conditions. This may be due to decreased ACE and TMPRSS2 mRNA expression in asthmatics on therapeutic drugs such as ICS and AIT acting as protective factors against SARS-CoV-2, in contrast to oral corticosteroid users. Overall, we noticed less prevalence of COVID-19 in asthmatics, possibly due to TH2-mediated reduced susceptibility.
Conclusion: There is apparent effectiveness of the current regimen to serve as protective factors for asthmatics, thereby making them less susceptible to COVID-19 to a clinically significant extent. However, more studies are required to show the evidence about decreased susceptibility of asthmatic patients to SARS-CoV-2.
Funding Source: No financial disclosures