Abstract
Introduction: Redo-Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (redo-SAVR) is the gold standard treatment for replacing degenerated Bioprosthetic Valves (BPV). Recently, Valve in Valve-Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (ViV-TAVI) has emerged as a less invasive alternative of redo-SAVR in high-risk patients. However, it’s efficacy is yet unclear and is to be explored further for wider adoption.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of meta-analysis studies comparing the safety and efficacy of ViV-TAVI versus redo-SAVR using the PubMed search engine from inception to May 2021 following the PRISMA guidelines. A meta-meta-analysis was performed by obtaining a pooled odds ratio, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) using a random effects model. I2 values of 25%, 50%, and 75% represented low, medium, and high heterogeneity.
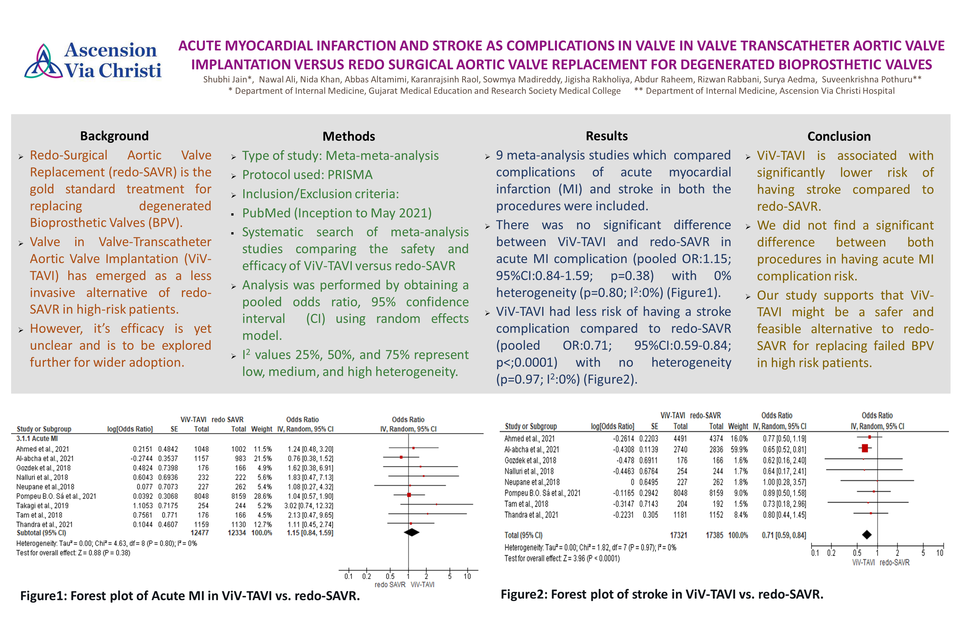
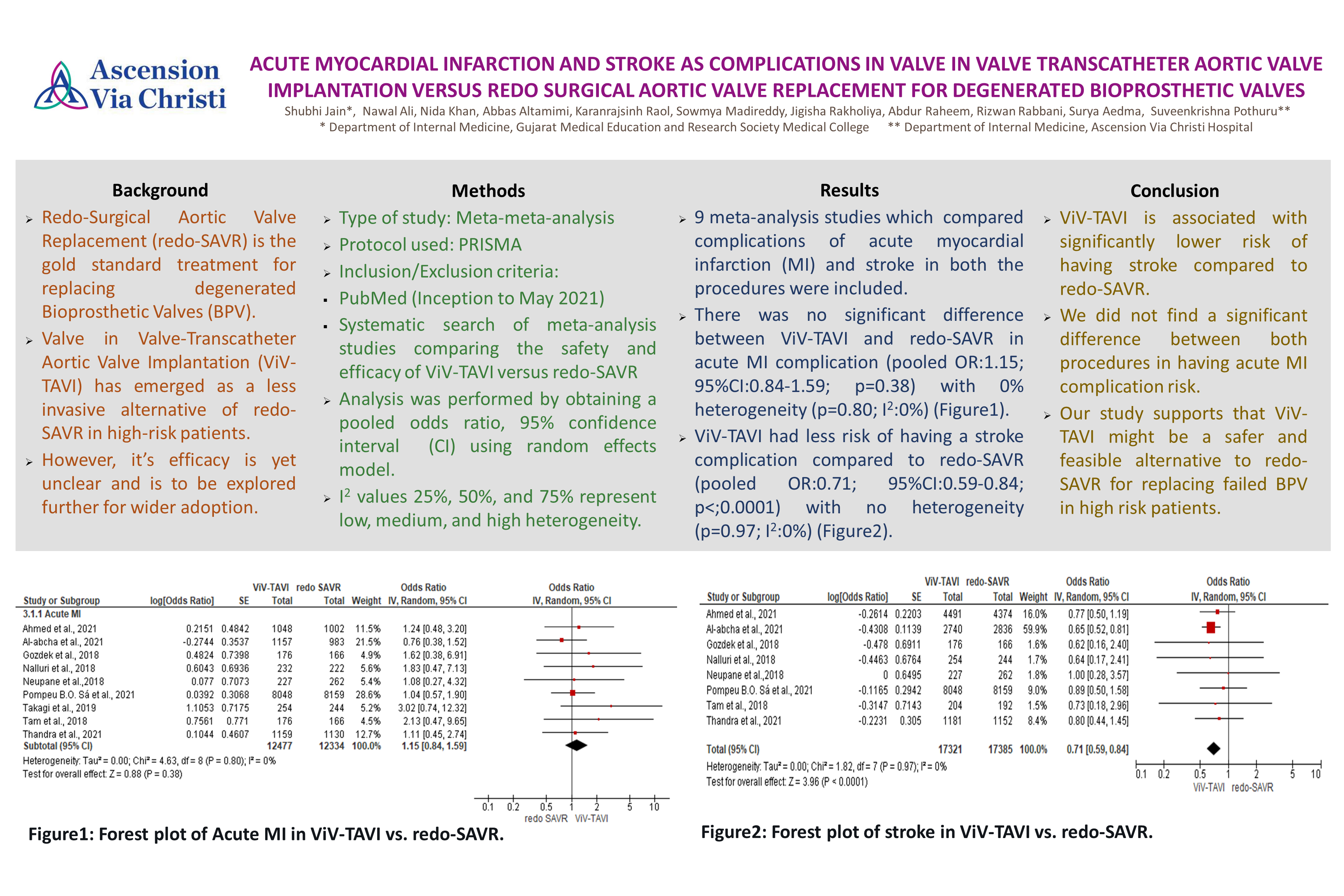
Results: Out of 20 meta-analysis screened, we have finally included 9 meta-analysis studies which reported comparison of complications of acute myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke in both the procedures. We found that there was no significant difference between Valve in Valve-Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation and Redo-Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in regards to acute myocardial infarction complication (pooled OR:1.15; 95%CI:0.84-1.59; p=0.38) with 0% heterogeneity (p=0.80; I2:0%). However, Valve in Valve-Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation had less risk of having a stroke complication (pooled OR:0.71; 95%CI:0.59-0.84; p<0.0001) with no heterogeneity (p=0.97; I2:0%) compared to Redo-Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement.
Conclusion: ViV-TAVI is associated with significantly lower risk of having stroke compared to redo-SAVR. But we did not find any significant difference between both groups in having acute MI complication risk. Hence, our study supports that ViV-TAVI might be a safer and feasible alternative to redo-SAVR for replacement of failed BPV in high risk patients.