Abstract
Background: Increased nutrition knowledge in children and adolescents can help them to consciously select healthy foods, which can have a long-term positive effect on their health. Serious games are immersive gaming technology platforms increasingly being used to train and educate people about nutrition.
Objective: The aim of this research was to determine whether serious games had an impact on the nutrition knowledge and behaviours of children and adolescents aged 4 to 18 years.
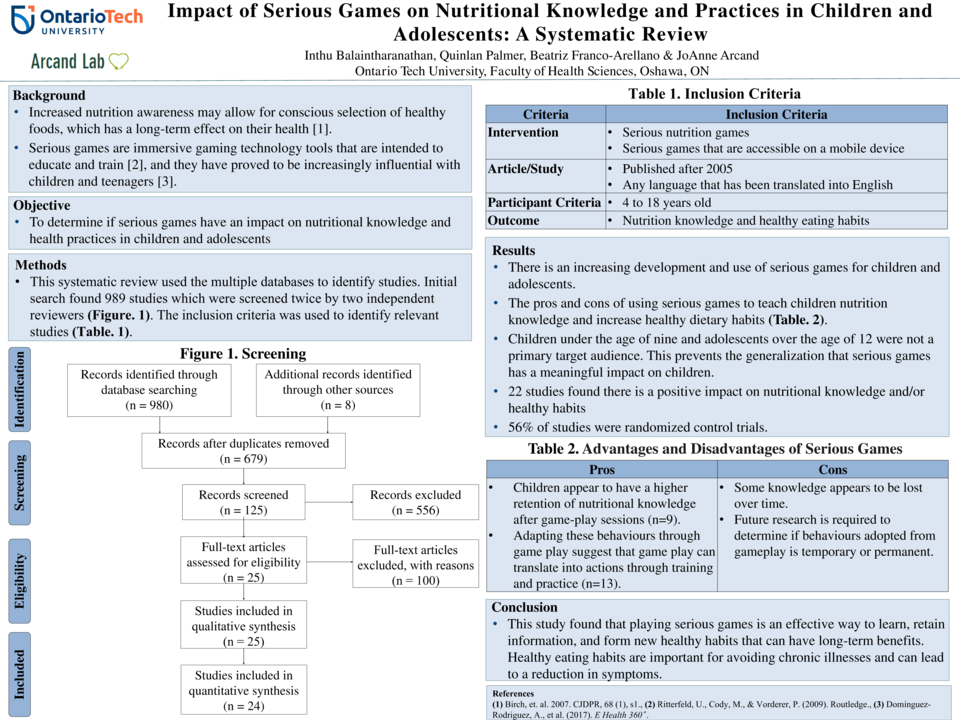
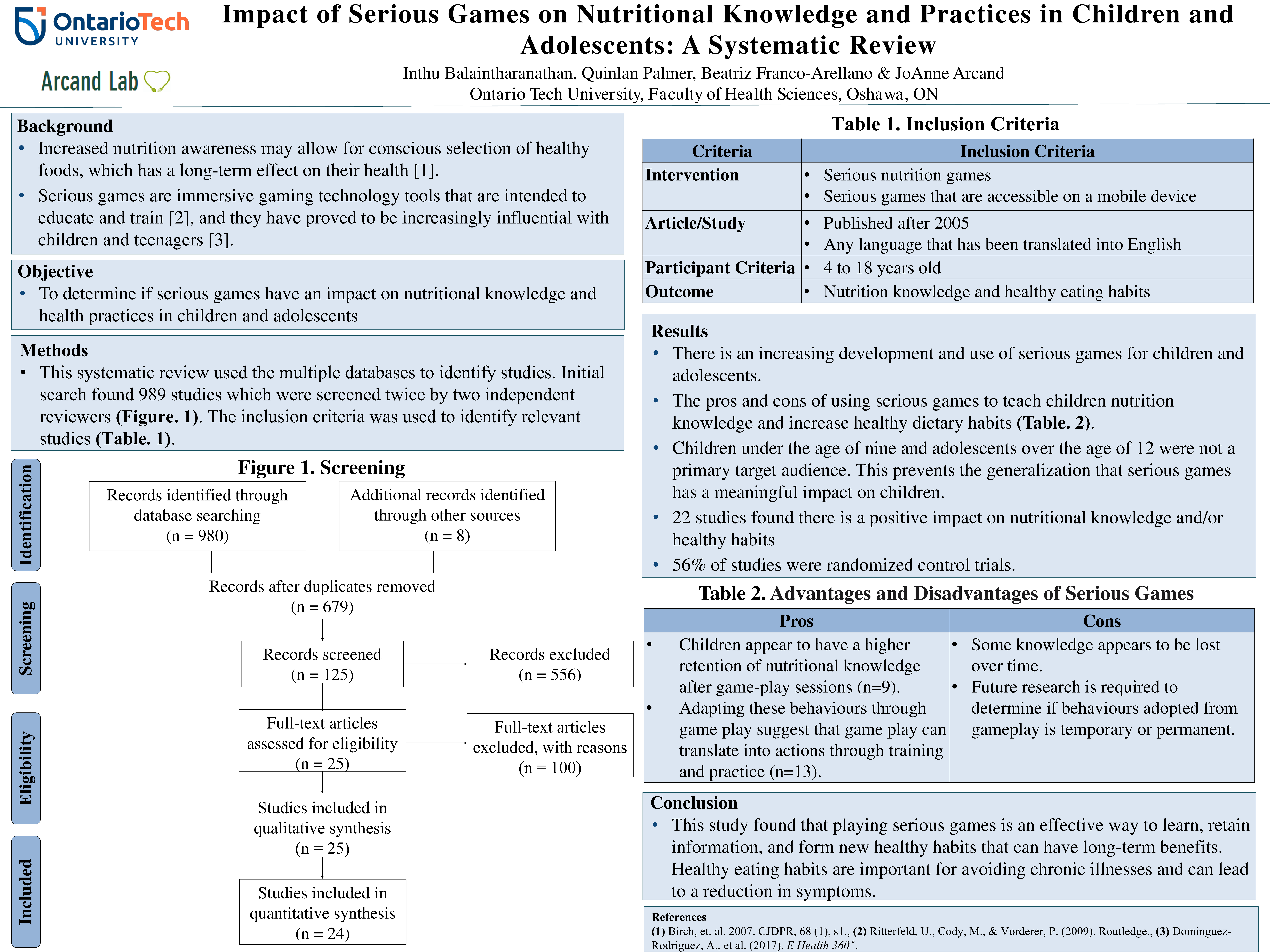
Method: This systematic review searched Google Scholar, PubMed, and EBSCOhost Research Databases and grey literature. To identify studies inclusion criteria included the use of serious mobile games to create nutritional knowledge and healthy eating habits, published after 2005, participants aged 4 to 18 years. Two reviewers sorted and analyzed the eligibility for this study.
Results: Initial search found 980 studies. A total of 679 unique articles were found after the removal of duplicated studies. A total of 24 studies were found eligible. 92% (n=22/24) found a positive impact on nutritional knowledge and/or healthy habits, measured by quizzes, questionnaires, and observations. Following game-play sessions, children tend to retain more dietary knowledge.
Conclusions: Children and adolescents appear to have higher retention of nutritional knowledge immediately after gameplay, which can translate into actions through the power of training and practice. This research has shown that using serious games can be used as an effective means of learning, retaining knowledge, and forming new healthy habits that can contribute to lifelong benefits. Further research is needed to determine how serious games can be integrated into society.