Abstract
Introduction: The outbreak of COVID-19 is escalating in the world. So, there is a need to recognize the laboratory predictors that could possibly assess the severity of the disease in the hospitalized patients.
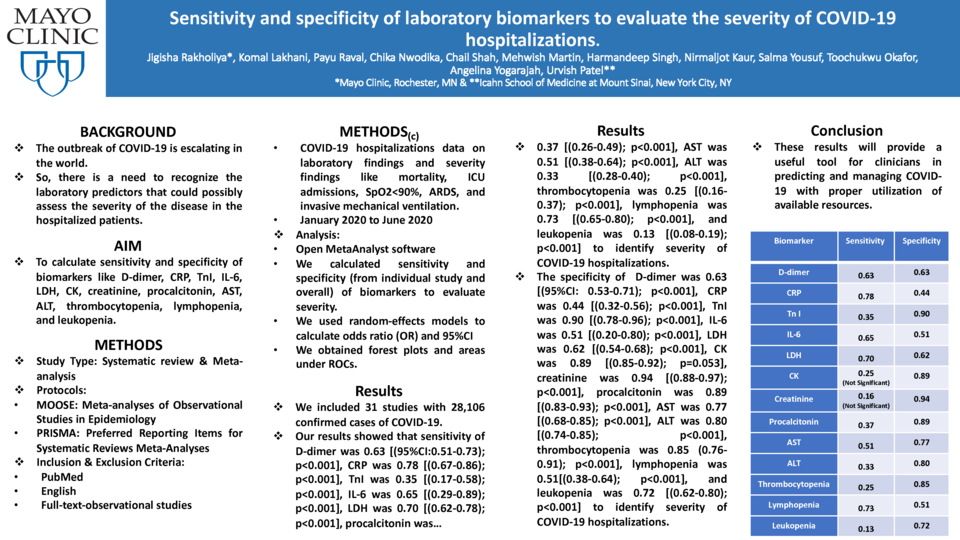
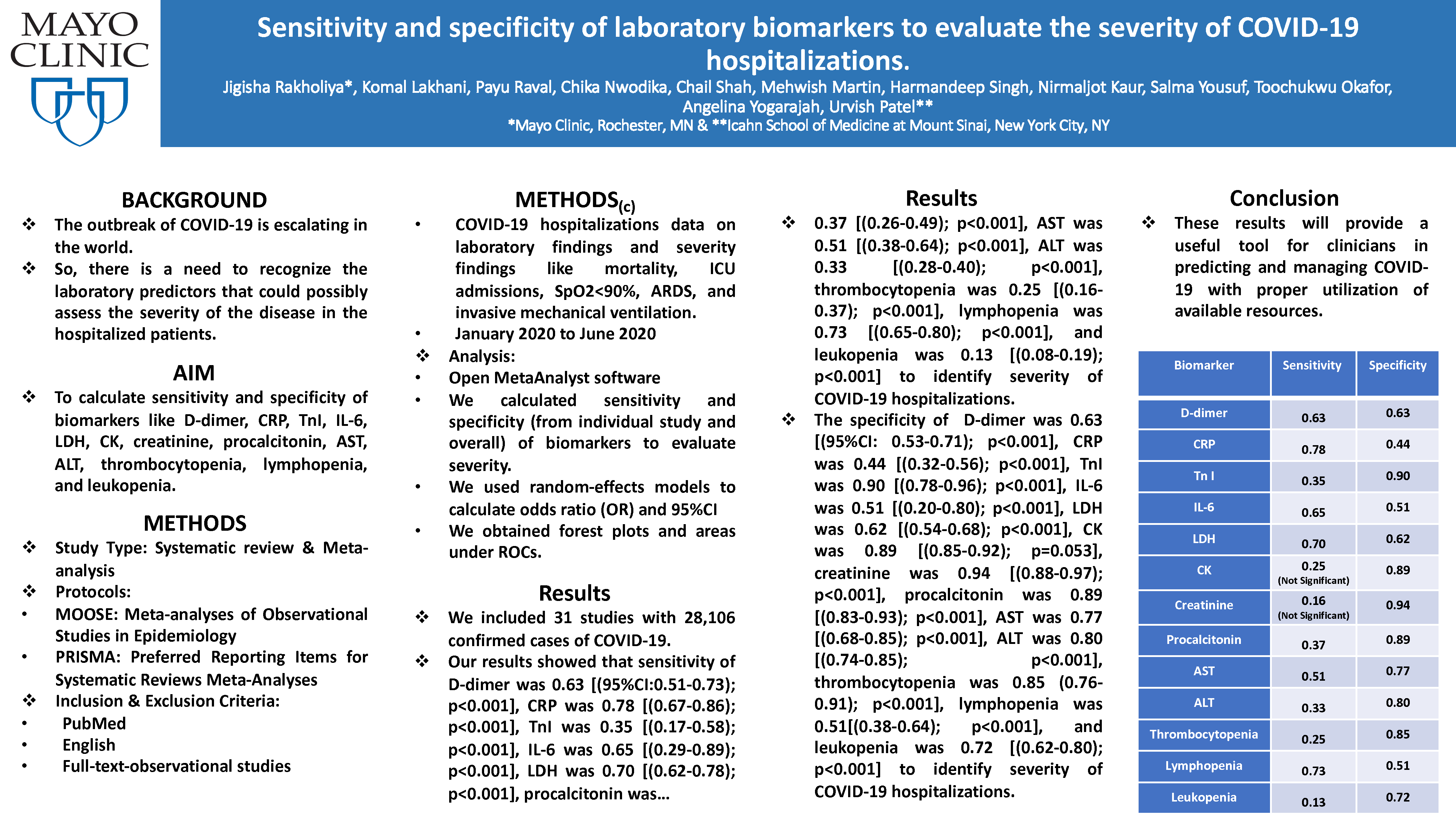
Aim: To calculate sensitivity and specificity of biomarkers like D-dimer, CRP, TnI, IL-6, LDH, CK, creatinine, procalcitonin, AST, ALT, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, and leukopenia.
Methods: By using Meta-analyses of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) protocols, we searched PubMed to identify English full-text-observational studies that had data on laboratory findings and severity findings like mortality, ICU admissions, SpO2<90%, ARDS, and invasive mechanical ventilation in COVID-19 hospitalizations between January 2020 to June 2020. Open MetaAnalyst software was used to calculate sensitivity and specificity (from individual study and overall) of biomarkers to evaluate severity. We used random-effects models to calculate odds ratio (OR) and 95%CI and to obtain forest plots and areas under ROCs.
Results: We included 31 studies with 28,106 confirmed cases of COVID-19. Our results showed that sensitivity of D-dimer was 0.63 [(95%CI:0.51-0.73);p<0.001], CRP was 0.78 [(0.67-0.86);p<0.001], TnI was 0.35 [(0.17-0.58);p<0.001], IL-6 was 0.65 [(0.29-0.89);p<0.001], LDH was 0.70 [(0.62-0.78);p<0.001], procalcitonin was 0.37 [(0.26-0.49);p<0.001], AST was 0.51 [(0.38-0.64);p<0.001], ALT was 0.33 [(0.28-0.40);p<0.001], thrombocytopenia was 0.25 [(0.16-0.37);p<0.001], lymphopenia was 0.73 [(0.65-0.80);p<0.001], and leukopenia was 0.13 [(0.08-0.19);p<0.001] to identify severity of COVID-19 hospitalizations. The specificity of D-dimer was 0.63 [(95%CI: 0.53-0.71);p<0.001], CRP was 0.44 [(0.32-0.56);p<0.001], TnI was 0.90 [(0.78-0.96);p<0.001], IL-6 was 0.51 [(0.20-0.80);p<0.001], LDH was 0.62 [(0.54-0.68);p<0.001], CK was 0.89 [(0.85-0.92);p=0.053], creatinine was 0.94 [(0.88-0.97);p<0.001], procalcitonin was 0.89 [(0.83-0.93);p<0.001], AST was 0.77 [(0.68-0.85);p<0.001], ALT was 0.80 [(0.74-0.85);p<0.001], thrombocytopenia was 0.85 (0.76-0.91);p<0.001], lymphopenia was 0.51 [(0.38-0.64);p<0.001], and leukopenia was 0.72 [(0.62-0.80);p<0.001] to identify severity of COVID-19 hospitalizations.
Conclusion: These results will provide a useful tool for clinicians in predicting and managing COVID-19 with proper utilization of available resources.