Abstract
Objectives: To utilize the RSSearch® Patient Registry (RSSPR) to compare local control (LC) and related toxicities in patients treated with either hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy (HSRT) or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for vestibular schwannomas (VS).
Methods: We searched the prospectively-maintained RSSPR for VS patients treated with SRS and HSRT from January 2008 to November 2016. Patients that had received previous surgery or radiation therapy were excluded. Potential factors predictive of toxicity and local control (LC) were estimated using time-to-event analysis and log-rank t-tests with the Kaplan-Meier method and a propensity-score weighted Cox proportional hazards model. Toxicity incidence was also analyzed with univariate and propensity-score weighted binary logistic regressions adjusting for all observable covariates.
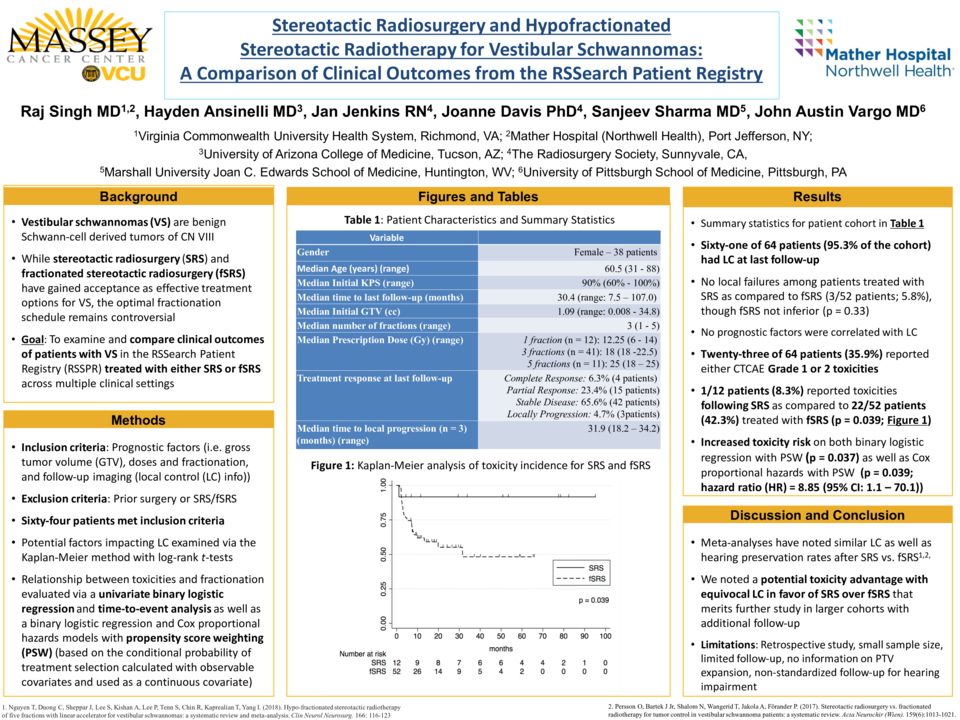
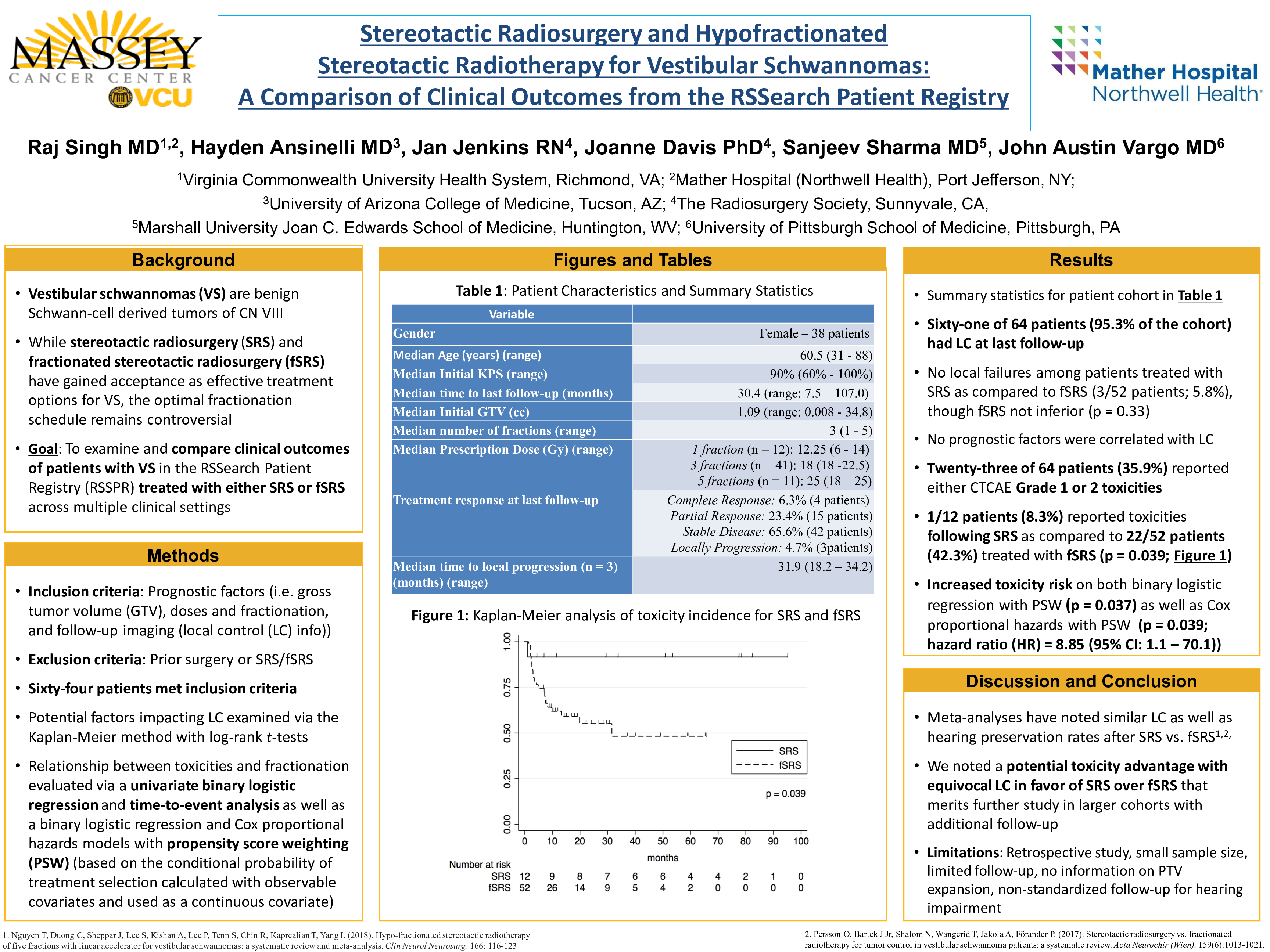
Results: Sixty-four patients were identified that met study criteria. Twelve patients were treated with SRS (median prescription dose of 12.25 Gy (range: 6-18 Gy)), 41 patients with 3 fractions (median prescription dose of 18 Gy (range: 18-22.5 Gy)), and 11 patients with 5 fractions (median prescription dose of 25 Gy (range: 18-25 Gy)). Median patient age was 60.5 years (range: 31-88) with a median time to last follow-up of 30.43 months (range: 7.53 - 106.97 months). The median GTV was 1.089cc (range: 0.00784 - 34.782). Sixty-one of 64 patients (95.3%) had radiographic local control at last follow-up. SRS (100%) and HSRT (94.2%) resulted in similar rates of LC (p = 0.33). Acute and late toxicities were reported by 35.9% of patients that were all Grade 1-2. HSRT was associated with a significantly higher likelihood of experiencing toxicities than SRS on time-to event analysis (42.3% vs. 8.33%; p = 0.038). The relationship between toxicity incidence and HSRT was maintained following a propensity score weighted binary logistic regression (p = 0.039) as well as a propensity score weighted Cox regression (p = 0.039; hazard ratio (HR) = 8.85 (95% CI: 1.12 - 70.10)).
Conclusions: SRS and HSRT in a multi-institutional cohort resulted in comparable LC consistent with prior single-institutional reports with fewer patients reporting toxicities following SRS.