Abstract
Purpose
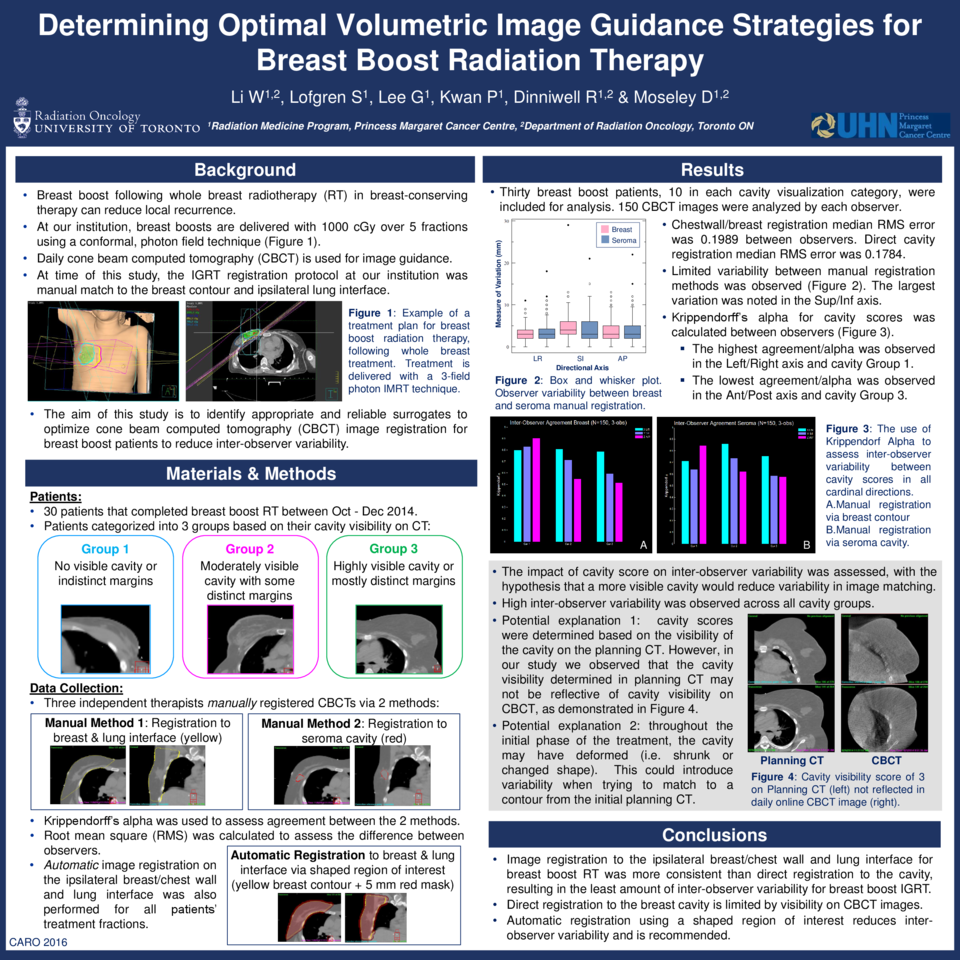
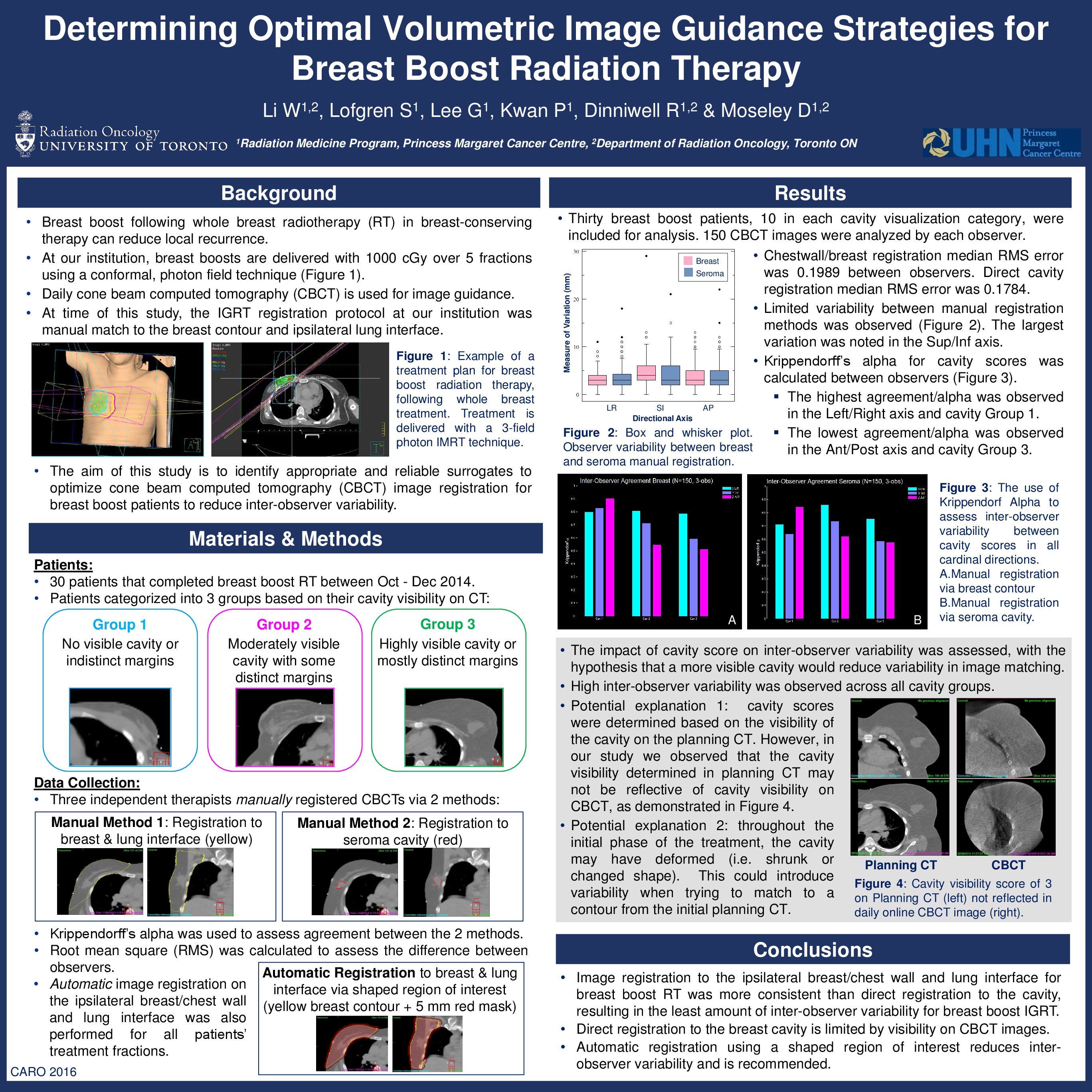
Breast boost following whole breast radiotherapy (RT) in breast-conserving therapy can reduce local recurrence. The aim of this study was to identify appropriate and reliable surrogates to optimize cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) image registration for breast boost patients to reduce inter-user variability.
Materials and Methods
Daily localization CBCT images are acquired and any positional discrepancies corrected prior to 3 field conformal breast boost treatment delivery. Under ethics approval, patients receiving breast boost RT between October and December 2014 were included in this retrospective analysis. Patients were categorized into 3 groups based on their cavity visibility on CT: C1 (indistinct or no visible cavity); C2 (moderately visible cavity with indistinct borders); and C3 (highly visible cavity). Three observers manually registered the CBCTs for each patient utilizing 2 methods: matching the ipsilateral breast/chest wall and lung interface as the target surrogate, and direct registration to the cavity. Krippendorff’s alpha was used to assess agreement between the 2 methods. Root mean square (RMS) was calculated to assess the difference between observers.
Results
Thirty breast boost patients, 10 in each cavity visualization category, were included for analysis. A total of 150 CBCT images were analyzed by each observer. Registration to the ipsilateral chestwall/breast reported a median RMS error of 0.1989 between observers. Direct registration to the cavity resulted in a median RMS error of 0.1784 between observers. The Krippendorff’s alpha for ipsilateral chestwall/breast registration in C1, C2 and C3 patients in the left-right(LR), cranio-caudal (CC), and anterior-posterior (AP) directions were: 0.8,0.84, 0.9; 0.81, 0.72, 0.55; and 0.78, 0.6, 0.52, respectively. The Krippendorff’s alpha for direct cavity registration in C1, C2 and C3 patients in the LR, CC, and AP directions were: 0.72, 0.64, 0.84; 0.86, 0.72, 0.62; and 0.75, 0.6, 0.58, respectively. The ranksum difference between registration methods was p=0.1538, with variations reported between cavity visualization categories (C1, p=0.8903, C2, p=0.0257, C3, p=0.9450).
Conclusions
Image registration to the ipsilateral breast/chest wall and lung interface for breast boost RT was more consistent than direct registration to the cavity, resulting in lower inter-observer variability for breast boost IGRT. Varying visibility on CBCT images limits direct registration to the breast cavity.